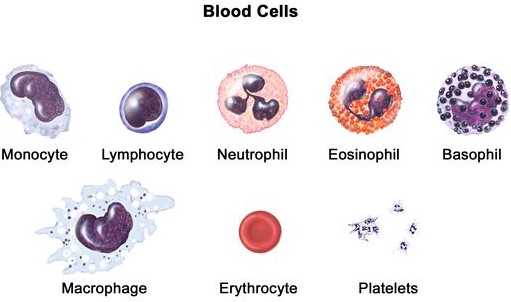
Differential leukocyte count (DLC)
Apparatus and reagents
- Anticoagulant added blood sample
- Clean glass slides
- Microscope
- Pasteur pipette
- Awash bottle for distilled water
- Leishmania stain
- Giemsa stain
- Dip quick stain
Principle
After the preservation of thin blood film with methanol for 3 minutes, the film is processed for staining. A blood film can be stained either with Leishmania, Giemsa, or Dip Quick stain. In contrast to the red blood cells, the white blood cells are nucleated and exist in several distinct types. The morphology and distribution percentage of polymorphs and agranulocytes should be examined under the oil immersion lens (X1000).Identification features
Granulocytes (Polymorphonuclear leukocytes)
1. Neutrophils
- 65 % of total WBCs
- 10 to 12 um diameter
- 3-5 lobed nucleus
- Small cytoplasmic granules
2. Eosinophils
- 2-4 % of total WBCs
- 13 um diameter
- Bilobed nucleus
- Cytoplasmic granules
3. Basophils
- 0.5 % of total WBCs
- 7 um diameter
- Bilobed nucleus
- Cytoplasmic granules
Agranulocytes (Mononuclear leukocytes)
4. Small lymphocytes
- 25 % of total WBCs
- 7 um diameter
- Very large, spherical nucleus surrounded by thick cytoplasm
- Non-granular cytoplasm
5. Large lymphocytes
- 3 % of total WBCs
- 10 um diameter
- Non-granular cytoplasm
6. Monocytes
- 3-7 % of total WBCs
- 15 um diameter
- Non-granular cytoplasm
Procedure
- Obtain a drop of blood by finger puncture.
- Place a small blood drop on one end of a clean glass slide.
- Keep this glass slide on a plane surface or hold it in a horizontal position between thumb and index finger.
- Hold a second slide (the spreader) at a 45-degree angle to the first slide and move it towards the drop of blood.
- Allow the blood to spread along the edge of the spreader slide.
- Move the spreader in a smooth, fast motion to the other end of the first slide.
- Allow the slide to air dry and place it on the staining rack.
- Using a medicine dropper or drop bottle pour 8-10 drops of Leishman's stain over the slide to cover the blood smear.
- Allow it to stand for 2 minutes.
- Add an equal number of distilled water drops from a drop bottle to dilute the stain.
- Mix the water and stain by tilting the slide first one way and then the other or by gently blowing on different places on the slide through a Pasteur pipette.
- Let the slide stain for 4-6 minutes.
- Drain off the diluted stain in a stream of distilled water from a wash bottle for about 20 seconds.
- Allow the slide to remain on the standing rack for 1-2 minutes, with the last wash covering it.
- Dry the bottom of the slide and allow the top to air dry by placing the slide against the support in an inclined position with the stained smear facing down.
- Place the slide on the fixed stage of the microscope and put a drop of cedarwood oil on the stained smear at a point about 2 cm from the start of the film.
- Examine the smear, first under low power, and then under oil immersion.
- Raise the body tube and swing the oil immersion lens (100X) into position.
- Watching from the side, bring the objective down slowly till it just enters the oil.
- Identify and count the number of each type of white cell on the slides.
- Count at least 100 WBCs (preferably 200 or 400) and calculate the percentage of each type of cell in the total count.

Comments
Post a Comment